Difference between revisions of "W3205 Quick Sort"
William-chin (talk | contribs) (Created page with " thumb == Background == * Read [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quicksort Quick Sort Algorithm] (Wikipedia) * View [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SLauY6PpjW4 Quick Sort Algorithm] (YouTube) * View [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7h1s2SojIRw Quick Sort Algorithm] (YouTube) == Introduction == The quicksort algorithm is generally known as one of the fastest sorting algorithms, many times faster than heap sort. If implemented well, quick so...") |
William-chin (talk | contribs) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== Choosing a Pivot == | |||
The pivot point which is chosen for the partition range and subranges will often determine the o complexity of the sort. Here is a list of common pivot points that are used: | |||
* Leftmost element | |||
* Median element | |||
* Rightmost element | |||
* Randomized element | |||
=== Implementation === | === Implementation === | ||
| Line 27: | Line 33: | ||
* First, create a partition | * First, create a partition | ||
* A partition will take the pivot point(x) and put all smaller elements before x, and all larger elements after x | |||
* in order to do this, we will need to keep track of the leftmost and rightmost index with 2 pointers( or markers) | |||
* While traversing elements, if we find a smaller element (an element smaller than x), we will swap the lower element to the left | |||
* Otherwise, if there aren't any smaller elements, we will ignore the current element | |||
* Then recursive calls of these partitions will be made until the array is sorted | * Then recursive calls of these partitions will be made until the array is sorted | ||
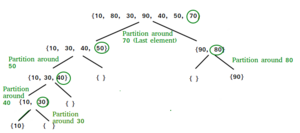
[[File:Quicksort algorithm diagram.png|thumb|right|Quicksort partition diagram]] | [[File:Quicksort algorithm diagram.png|thumb|right|Quicksort partition diagram]] | ||
=== Performance === | === Performance === | ||
Latest revision as of 09:35, 3 May 2022
Background[edit]
- Read Quick Sort Algorithm (Wikipedia)
- View Quick Sort Algorithm (YouTube)
- View Quick Sort Algorithm (YouTube)
Introduction[edit]
The quicksort algorithm is generally known as one of the fastest sorting algorithms, many times faster than heap sort. If implemented well, quick sort algorithms can have a complexity of O(n log n)
Algorithm[edit]
The quicksort algorithm calls for a pivot during its recursive calls, here is an overview:
- Pick an element as a pivot
- Create 2 markers, which will be compared with a < function in order to set values up for a partition
- Create a partition, which will be used to put elements in an array smaller than x and greater than x
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until the array is sorted
Choosing a Pivot[edit]
The pivot point which is chosen for the partition range and subranges will often determine the o complexity of the sort. Here is a list of common pivot points that are used:
- Leftmost element
- Median element
- Rightmost element
- Randomized element
Implementation[edit]
Quicksort algorithms vary, partitions and pivot elements can be different for each algorithm. The partition and method of obtaining a pivot element usually depend on what is being sorted, and what level of Big O complexity the algorithm is aiming for.
- First, create a partition
- A partition will take the pivot point(x) and put all smaller elements before x, and all larger elements after x
- in order to do this, we will need to keep track of the leftmost and rightmost index with 2 pointers( or markers)
- While traversing elements, if we find a smaller element (an element smaller than x), we will swap the lower element to the left
- Otherwise, if there aren't any smaller elements, we will ignore the current element
- Then recursive calls of these partitions will be made until the array is sorted
Performance[edit]
As seen before, the average performance of quicksort is O(n log n) complexity, but how quicksort algorithms work, depends on the method of obtaining a pivot point, and how partitions are made (based on how array elements were originally inputted), quicksort can have a worse case complexity of O(n^2).
Exercises[edit]
- M1352-10 Complete Merlin Mission Manager Mission M1352-10.