W3150 Graphs
Overview[edit]
In Computer Science, Graphs refer to a Data Structure meant to store Data involving Nodes and their relationships. Specifically, a Graph is made of several points typically called Vertices with relationships in between them called Edges. This data structure can be very useful in applications where the relationships between the data bares an importance similar to the data that's being stored. Using the Edges between the Vertices, information can be mathematically conveyed.
For instance, you may have heard of Graphs in the past in the context of Graph Theory, which is the study of graphs for finding mathematical relationships between objects. A concept in Graph Theory is a Path, which simply refers to the series of edges that connect two given Vertices. Simply understanding the path between vertices can provide information on the data such as finding which vertices are the most and least inter-connected.
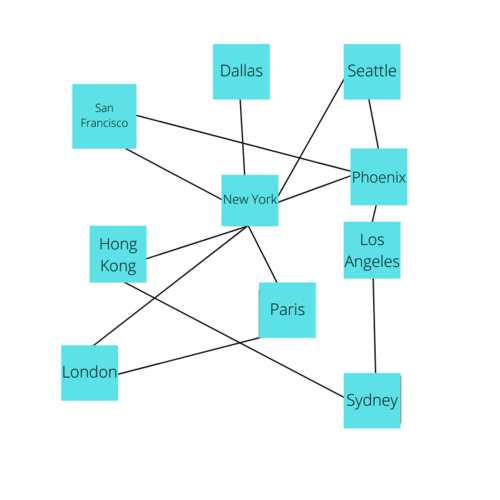
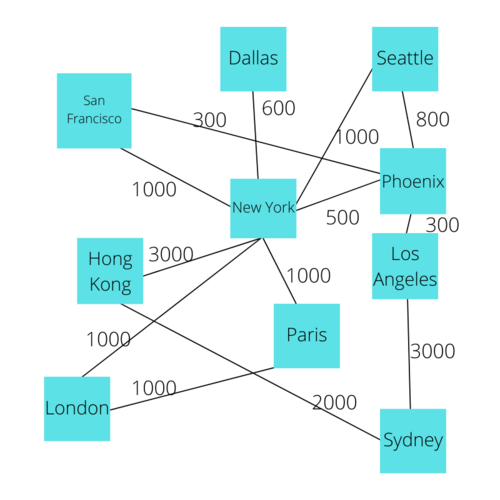
This type of information can be very useful for data analysts, software developers, and even enterprise applications. For instance, a common example of Graph usage is the flights at an Airline where the Vertices represent different locations and edges represent an available flight between them.
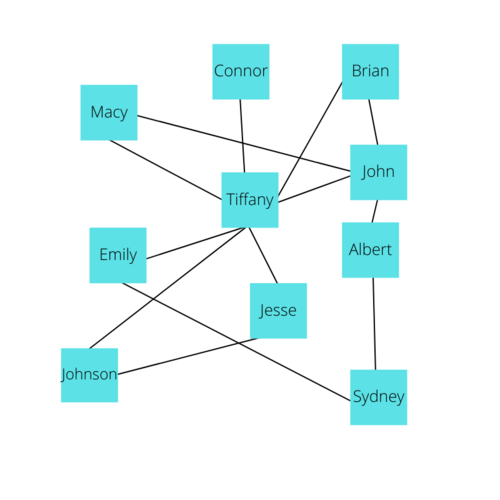
Graphs can also be used for social networking applications where a Vertex is a user and an edge is a relationship between them.
You can imagine that in either of these scenarios, understanding the inter-connectedness of a given Vertex can provide important insights. such as finding cities with greater air traffic or users with the strongest business connections, and that's only one value that can be derived from one feature of a graph. With the concepts of Weight, Direction, and Path, graphs prove to be one of the most dynamic and insightful forms of storing data.
Looking at these graphs, you might also notice that they are in many ways similar to a Linked List since the underlying concept is the same: many nodes of data with pointers in between that data. The main difference is Graphs are rarely, if ever, linear in nature. Now with that, we'll take a deep dive on how Graphs work as well as how to implement one using Swift.
Adjacency[edit]
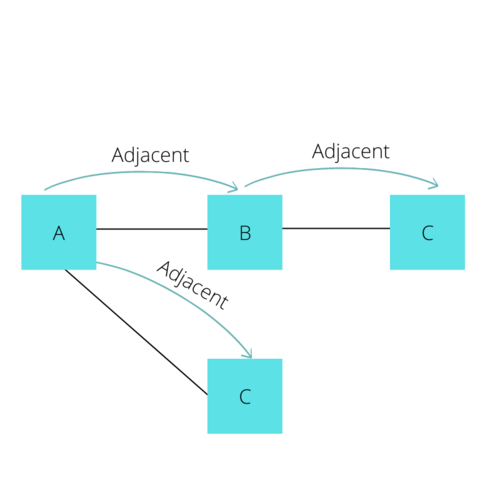
First, let's understand Adjacency, a term commonly used when discussing Graphs. Adjacency in a graph essentially means if a vertex has an edge connecting it to another vertex. In the following Diagram, A is adjacent to B, B is adjacent to A and C, but A is not Adjacent to C since there is not an edge that directly connects these two.
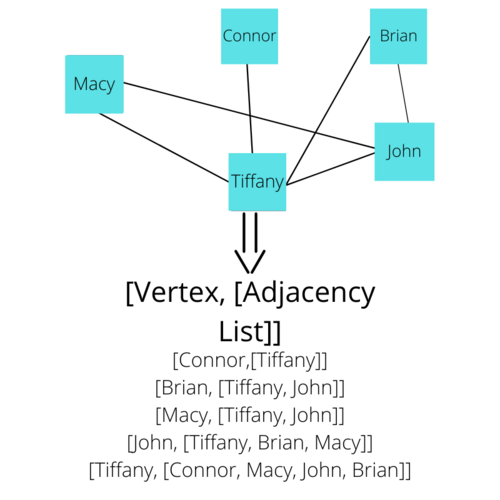
Now, from the idea of Adjacency, we can make an Adjacency List. Each Vertex will have an Adjacency List which describes every Vertex that is adjacent to the given vertex. In other words, you can make an Adjacency List by looking at each individual vertex and documenting all of the vertices it shares an edge directly with. The Adjacency Lists combined with a List of all the vertices can essentially describe a Graph. Here is a visual representation of the Adjacency Lists for every Vertex in the Social networking example.
Adjacency Lists will be critical for implementing the code to build our Graph later on.
Quiz[edit]
Types of Edges[edit]
Now, let's take a deeper look at Edges. Graphs can have specialized edges for different use cases. Specifically, their can be Weighted Edges. Where the edges are given greater emphasis by assigning a numerical value to the edge giving it weight. This way, you can look at an edge that has the highest value of 10 and look at an edge that has a lowest value of 1 and be able to interpret a difference in the importance of the relationship between the respective vertices.
Let's look at the Social Networking and Airline examples again. If two users are friends, this relationship can be represented by a max weight on the edge, such as the number 1, then we can have the weight be the number 2 between two users who are connected only by a mutual friend. This principle could be used to implement the sort of Connection functionality that popular apps such as LinkedIn uses, where the app shows if the user is a 1st, 2nd, or 3rd connection. We can also assign values to the edges of an Airline graph to represent the cost of a certain flight.
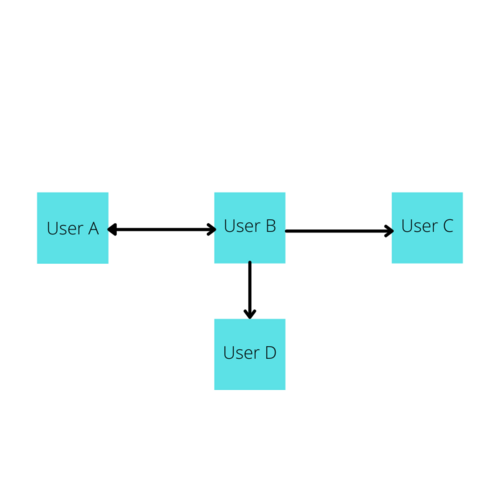
Beyond the concept of Weight, edges can also have direction. For instance, perhaps user A is subscribed to user B, but user B is not subscribed to user A. This can be stored in the graph via direction and would be visualized with an image such as the following.
You can implement this concept in code by having a "From:" and a "To:" or a "Source:" and a "Destination:" when describing the Adjacency Lists, this will be explored more in the next section. Note: If an edge does not have a direction, it's usually implied that it is bi-directional, such as a Mutual connection on a social network or an Airline that flies Airplanes both to and from a certain location.
Quiz[edit]
Making a Graph[edit]
As was mentioned, Graphs are made of Vertices and Edges. So, let's start by making some basic classes to handle a Vertex and an Edge. For this example, we'll keep things as simple as we can, but keep in mind there are many ways of tackling the implementation of a graph. You should challenge yourself to learn other implementations as well.
public class Vertex{
var data: String?
var adjacencyList: Array<Edge>
init() {
self.adjacencyList = Array<Edge>()
}
}
Notice that each Vertex will need to hold an Array listing all of the Edges it is adjacent with, this is one of the many ways of implementing adjacency lists.
We'll also include the following function as well to get the data stored in the vertex class
func getData() -> String{
return data!
}
public class Edge{
var weight: Int
var to: Vertex
var from: Vertex
init(){
weight = 0
self.to = Vertex()
self.from = Vertex()
}
}
Here, we'll implement both direction and weight by having properties for such in each Edge. Now, all we need to do is make a Graph class that has some basic functions to let us interact with these classes.
public class Graph{
func addVertex(data: String) -> Vertex {
let newVertex: Vertex = Vertex()
newVertex.data = data
return newVertex
}
func addEdge(from: Vertex, to: Vertex, weight: Int){
let newEdge = Edge()
newEdge.to = to
newEdge.weight = weight
from.adjacencyList.append(newEdge)
}
}
Here we have two functions. One to add a Vertex and one to add an Edge in between two vertexes. We simply make a new vertex and assign the data value to the given value and the same is true of the Edge. Now, we can test this mini graph.
let socialNetwork = Graph()
let user1 = socialNetwork.addVertex(data:"Tiffany")
let user2 = socialNetwork.addVertex(data:"Connor")
socialNetwork.addEdge(from: user1, to: user2, weight: 10)
socialNetwork.addEdge(from: user2, to: user1, weight: 10)
print(user1.getData())
print(user2.getData())
Here we set up two users and put an edge in between them, then print out each user to make sure the scripts work. This remains a somewhat crude example however it has the basic features of a graph. As a bonus challenge, you can try to print out the adjacency lists of a user as a String. Think of the additional functions and refactoring you may need.
Quiz[edit]
Key Concepts[edit]
- Graphs are a data structure meant to show relationships between data using Vertices and Edges
- A Graph can be described by using Adjacency Lists, which is a list of all the Vertices a given Vertex is connected to
- The weight on edge can show the relative importance of the relationship between two given Vertices
- An Edge can also have direction (From: A To: B) to better describe the relationship between Vertices