W2707 Model View Controller
Background[edit]
A software design pattern is a general, reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem in software design. It provides a template that can be used to solve similar problems in various situations. Design patterns can help speed development by providing tested and proven paradigms. A paradigm is defined as a method used to solve a problem or complete a task. A programming paradigm is a paradigm that coders implement in programming language tools and techniques. Some examples of programming paradigms include Imperative, Declarative, and Model-View-Controller. In the case of the Model-View-Controller (MVC) paradigm, you can use it to understand how code is managed in an application, how data is handled in the database, and how that data is visually represented via the communication between the two through a controller.
Introduction[edit]
The Model-View-Controller, or MVC, is a popular way to organize code for apps and websites that have a user interface. The idea is that portions of the code are grouped into different objects that serve different functions. This makes it much easier for collaborators to understand the code's purpose and where future material should be added. These three objects are Model, View, and Controller.
Description[edit]
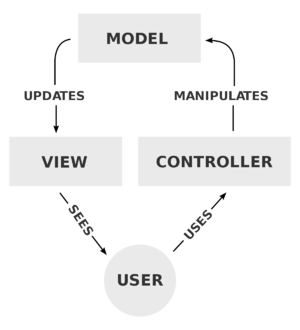
The main idea of the MVC pattern is designating a unique purpose to different sections of your code. In brief, the Model can be thought of as the data. The View can be thought of as the user interface. The Controller can be thought of as an input reader that takes the user input and decides what to do with it. The MVC model can be seen as a cycle where everything contributes to another's task. Without one of them, the program would be incomplete.
Model[edit]
The Model is the collection of tasks that contain the functionality of a program. This section can be seen as the brains of the code because it contains all the data, logic, and rules of the application. For example, when the user clicks a button, the model does something in response to the input and sends the output to the controller.
View[edit]
The View contains the user interface. This section is primarily focused on the visuals that a user sees, such as the font or color on the screen. It also stores the functions that define the way users use the app are stored here. The user's information requests are transferred from the View to the Model by the Controller. For example, the look of a button.
Controller[edit]
The Controller is the primary connection between the Model and View. Whereas the View focuses on presenting and taking information to and from the user. And the Model manipulates the data, rules, and logic of the application. The Controller is the middleman that takes the input from the View and updates the Model. The Controller basically acts as a "conduit" or a connection between the View and the Model. It interprets the input from the View to and sends data to the Model.
[jeff] The Model of a program would be the data and the logic of the program. The controller is the ‘middle-man’ between the model and the view. The view is the appearance of the application, which is created after the controller has received the necessary data to display to the user. The View represents the data visually and contains the functions that enable users to interact with a user interface. An example of this would be when you are customizing your desktop’s wallpaper to make it visually appealing. An important fact of this component is that it only demonstrates visuals given to it as instructions from the controller. There is no data logic being analyzed by the View as that function will already occur in the Controller. The Controller is the brains of the program. The only interaction between the Model and the View is through the Controller. Any user input is given to the controller which it translates into a request for the model to process. The controller then takes the data from the model and passes it to the view to display.
Example[edit]
One example of a Model View Controller that you might be familiar with is Super Mario Bros. A model is data used in a game, so the actual data that represents the character Mario would be the model in MVC. The view is the visuals in Super Mario Bros. From the background to the platforms and designs of characters, the view would be the visual aspects of the game. The controller handles the inputs, so anything from a Wii Remote to a Switch Controller could be examples of the controller that helps the user interact with the game and make Mario move. All of these work together in order to make all the aspects of Super Mario work efficiently.
Paradigm[edit]
A paradigm is a model or pattern that can be used to represent a certain concept, Having a model to represent a universal concept allows a person to understand the inner-workings behind any application. In the case of the Model-View-Controller paradigm, you can use it to understand how code is managed in an application and how data is handled between the database, and how that data is visually represented via the communication between the two through a controller. These applications can range from being a website to a video game like Super Mario Bros to websites like YouTube. Overall, a paradigm sets the standards for an accepted idea (in this case, MVC).
Sources[edit]
https://www.codecademy.com/articles/mvc https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DUg2SWWK18I https://www.educative.io/blog/mvc-tutorial
Presented by Team Cambodia