Difference between revisions of "REST - Wendy's 4 for 4"
Kian-durrett (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
The body is the contents of the resource, and conveniently uses the JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) as the format. Both Creation operations and Update operations contain a body, but a Retrieval operation does not contain a body. In addition, the Deletion operation would also not contain a body. | The body is the contents of the resource, and conveniently uses the JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) as the format. Both Creation operations and Update operations contain a body, but a Retrieval operation does not contain a body. In addition, the Deletion operation would also not contain a body. | ||
* '''Header''' | * '''Header''' | ||
A header in short is simply a description of the resource, essentially acting as | A header in short is simply a description of the resource, essentially acting as metadata for the resource. | ||
== Usage == | == Usage == | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
The server will not keep the latest HTTP request the client made. Every request will be given equal importance or in other words be “new”. | The server will not keep the latest HTTP request the client made. Every request will be given equal importance or in other words be “new”. | ||
* '''Cacheable''' | * '''Cacheable''' | ||
Caching shall be applied to resources when acceptable, and then these resources must call themselves cacheable to avoid extra client-server interactions and using caching in general can eliminate client-server interactions, improving scalability and performance. | Caching shall be applied to resources when acceptable, and then these resources must call themselves cacheable to avoid extra client-server interactions, and using caching, in general, can eliminate client-server interactions, improving scalability and performance. | ||
* '''Layered system''' | * '''Layered system''' | ||
REST uses a layered system architecture where you assign the APIs on server A, and store data on server B and complete requests in Server C for example. | REST uses a layered system architecture where you assign the APIs on server A, and store data on server B, and complete requests in Server C for example. | ||
* '''Code on demand (optional)''' | * '''Code on demand (optional)''' | ||
Clients may use your API to get a UI widget rendering code that can be rendered directly in the code of MVC views. | Clients may use your API to get a UI widget rendering code that can be rendered directly in the code of MVC views. | ||
Revision as of 10:46, 20 August 2021
[1]== Brief Overview ==
REST API or RESTful API stands for REpresentational State Transfer
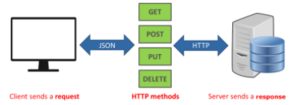
An API is a means of communication with a server. Whenever you browse something on the internet, your browser will ask the server for data. The server will then present the data; an API handles the data transfer between your device and the server.
The rest API works with the client and server. The client will send data through a request, and the server will send the data back in the form of a response.
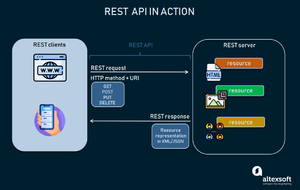
To view, an image of how RESTAPI works click here[[1]]
Components[edit]
- Resource Path
Resource path is the “request target” or the desired destination for the object. For example, a resource path could be “codermerlin.com/wiki/database/grades” where the object would be sent to the grades directory of the host.
- HTTP Verb
With an HTTP Verb, the actions of the resource could be easily defined. A handy acronym to remember the available HTTP Verbs is “C R U D” or Creation (creates a resource), Retrieval (retrieves a resource), Update (updates a resource), and Deletion (deletes a resource).
- Body
The body is the contents of the resource, and conveniently uses the JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) as the format. Both Creation operations and Update operations contain a body, but a Retrieval operation does not contain a body. In addition, the Deletion operation would also not contain a body.
- Header
A header in short is simply a description of the resource, essentially acting as metadata for the resource.
Usage[edit]
REST has become increasingly popular due to its data structure requiring less bandwidth (Maximum amount of data transferred over time), making it much more efficient at transferring data. As a result, REST is often used on many web services and more recently, cloud services.
additional Concepts & challenges[edit]
Restrictions[edit]
- Uniform interface
All resources should be obtained by using a common method such as HTTP GET and similarly manipulated using a common approach.
- Client–server
Client application and server application must be able to function separately and the client should know only the resource URL.
- Stateless
The server will not keep the latest HTTP request the client made. Every request will be given equal importance or in other words be “new”.
- Cacheable
Caching shall be applied to resources when acceptable, and then these resources must call themselves cacheable to avoid extra client-server interactions, and using caching, in general, can eliminate client-server interactions, improving scalability and performance.
- Layered system
REST uses a layered system architecture where you assign the APIs on server A, and store data on server B, and complete requests in Server C for example.
- Code on demand (optional)
Clients may use your API to get a UI widget rendering code that can be rendered directly in the code of MVC views.