Number Systems
Number Systems[edit]
Positional Notation[edit]
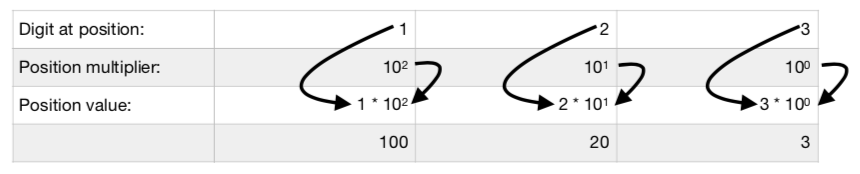
Positional notation (sometimes called place-value notation) is a method of encoding numbers. It differs from other notations (such as Roman numerals) in that it uses the same symbol for different orders of magnitude depending on its position. For example, consider the number 23. The “3” indicates 3 ones, because it is in the ones position. The “2”, however, indicates 2 tens, because it is in the tens position. We know the value of a position by its location within the number. As we move left in a number, each position is valued at ten times the prior position. It might help if we label each position using power notation. Consider the number 123:
The “3” is the right-most, and therefore the lowest-valued position, representing “ones” with a position multiplier of 100 (that is, 10 raised to the zero power, or 1). The “2” is located one position to the left, so we multiply by 10 again giving us a position multiplier of 101 (that is, 10 raised to the first power, or 10). Finally, the “1” is located one position to the left, so we again multiply by 10 giving us a position multiplier of 102 (that is, 10 raised to the second power, or 100). By multiplying each digit by its corresponding position multiplier, we can obtain the value of the entire number:
1 * 102 + 2 * 101 + 3 * 100 =
100 + 20 + 3 =
123
While we generally understand the mechanics of this process in the decimal system, thinking about how it actually works will enable us to consider other systems.
Number Base[edit]
The radix or base is the number of unique digits, including zero, used to represent numbers in a positional numeral system. The base is normally written as a subscript to the right of the number. For example, the decimal number 123 would formally be written as (123)10
Note that the parentheses are sometimes not written: 12310
In the case of decimal (base 10) numbers, the subscripted 10 is often assumed and not written.
Decimal System[edit]
The decimal system is the system with which we are most familiar. It is a decimal system because it contains ten unique digits:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
For any (integer) value larger than 9, we’re required to use positional notation. Please keep in mind that “10” is not a digit. Rather, it’s a number consisting of two digits, a “1” in the tens (101) position and a “0” in the ones position (100).
Octal System[edit]
The octal system uses eight unique digits to represent a number:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Let’s consider the value of an octal number: 47358
What is the decimal value of this number? We use exactly the same method that we use for knowing the value in any system:
| Digit at position: | 4 | 7 | 3 | 5 |
| Position multiplier: | 83 | 82 | 81 | 80 |
| Position value: | 4 • 83 | 7 • 82 | 3 • 81 | 5 • 80 |
| 2048 | 448 | 24 | 5 |