Discrete Mathematics
Introduction[edit]
Discrete Mathematics is a branch of mathematics that is concerned with “discrete” mathematical structures. It provides an essential foundation for virtually every area of computer science and its applications are vast. It is increasingly being applied in the practical fields of mathematics and computer science. Discrete mathematics is in contrast to continuous mathematics, which deals with structures which can range in value over the real numbers, or have some non-separable quality. Discrete Mathematics concerns itself mainly with finite collections of discrete objects. With the growth of digital devices, especially computers, discrete mathematics has become more and more important. Discrete mathematics is the mathematical language of computer science, and as such, its importance has increased dramatically in recent decades.
[edit]
- Combinatorics
Combinatorics is often concerned with how things are arranged. In this context, an arrangement is a way objects could be grouped. The most basic rules regarding arrangements are the rule of product and the rule of sum.
Sum Rule Principle[edit]
Assume some event E can occur in m ways and a second event F can occur in n ways, and suppose both events cannot occur simultaneously. Then E or F can occur in m + n ways. In general, if there are n events and no two events occurs in same time then the event can occur in n1+n2..........n ways.
Product Rule Principle[edit]
Suppose there is an event E which can occur in m ways and, independent of this event, there is a second event F which can occur in n ways. Then combinations of E and F can occur in mn ways. In general, if there are n events occurring independently then all events can occur in the order indicated as n1 x n2 x n3.........n ways.
Permutation[edit]
A permutation is an arrangement of some elements in which order matters.
Any arrangement of a set of n objects in a given order is called Permutation of Object. Any arrangement of any r ≤ n of these objects in a given order is called an r-permutation or a permutation of n object taken r at a time.
It is denoted by P (n, r) 
Combination[edit]
A combination is an arrangement of objects without regard to order. The number of all combinations of n things, taken r at a time is C (n, r)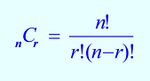
- Set Theory
- Graph Theory
- Mathematical Induction
- Boolean Algebra
- Probability Theory
- Group theory
