Boolean Algebra
From Coder Merlin
Revision as of 18:48, 16 March 2019 by Chukwuemeka-tinashe (talk | contribs)
Within these castle walls be forged Mavens of Computer Science ...
— Merlin, The Coder
Boolean Algebra[edit]
Background[edit]
The branch of algebra in which the values of the variables are the truth values true and false, usually denoted 1 and 0 respectively. It is a formal description of logical relations. It was introduced by George Boole in his first book The Mathematical Analysis of Logic in 1847.
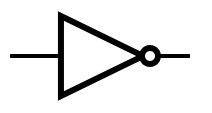
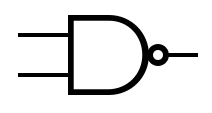
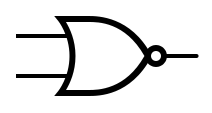
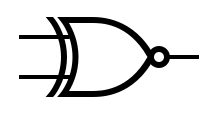
Logic Gates[edit]
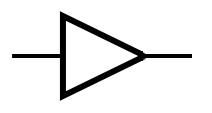
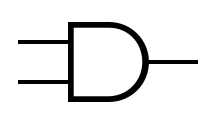
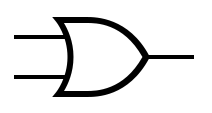
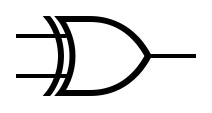
An idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function; that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more binary inputs and produces a single binary output.
Composition[edit]
Logic gates can be cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed, allowing the construction of a physical model of all of Boolean logic.
References[edit]
- Boolean Algebra (Wikipedia)
- De Morgan's Laws (Wikipedia)
- Logic Gates (Wikipedia)