Difference between revisions of "Boolean Algebra"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=== Logic Gates === | === Logic Gates === | ||
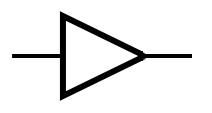
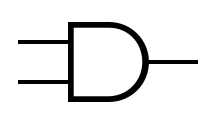
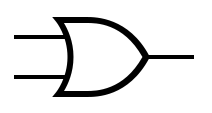
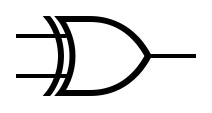
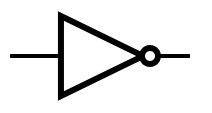
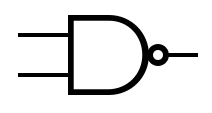
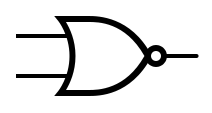
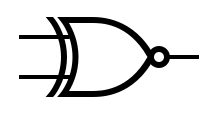
An idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function; that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more binary inputs and produces a | An idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function; that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more binary inputs and produces one or more binary outputs. | ||
== Truth Tables == | |||
'''Truth tables''' provide us with a straightforward means to specify the required output(s) for the specified input(s), in table form. On the left-hand side of the table we enumerate the input(s) and on the right-hand side of the table we specify the output(s). Assuming that we have <math>n</math> inputs we may label each input as <math>I_1, I_2, I_3, ... I_n</math>. The value of the inputs on any given row, may be referred to as an '''input tuple'''. Likewise, assuming that we have <math>m</math> outputs we may label each output as <math>O_1, O_2, O_3, ... O_n</math>, and the value of these outputs on any given row may be referred to as an '''output tuple'''. The number of rows in any such table is given by the formula <math>2^n</math>. | |||
{{Question| | |||
Why is the formula for determining the number of rows in a truth table related only to the number of inputs, and why is the formula <math>2^n</math>? | |||
}} | |||
Note that for convenience we sometimes label inputs as A, B, C, etc. rather than <math>I_1, I_2, I_3,</math> etc. and do the same for outputs, often beginning with the letter Q. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 15:41, 20 June 2019
Background[edit]
The branch of algebra in which the values of the variables are the truth values true and false, usually denoted 1 and 0 respectively. It is a formal description of logical relations. It was introduced by George Boole in his first book The Mathematical Analysis of Logic in 1847.
Logic Gates[edit]
An idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function; that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more binary inputs and produces one or more binary outputs.
Truth Tables[edit]
Truth tables provide us with a straightforward means to specify the required output(s) for the specified input(s), in table form. On the left-hand side of the table we enumerate the input(s) and on the right-hand side of the table we specify the output(s). Assuming that we have inputs we may label each input as . The value of the inputs on any given row, may be referred to as an input tuple. Likewise, assuming that we have outputs we may label each output as , and the value of these outputs on any given row may be referred to as an output tuple. The number of rows in any such table is given by the formula .
Why is the formula for determining the number of rows in a truth table related only to the number of inputs, and why is the formula ?
Note that for convenience we sometimes label inputs as A, B, C, etc. rather than etc. and do the same for outputs, often beginning with the letter Q.
Composition[edit]
Logic gates can be cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed, allowing the construction of a physical model of all of Boolean logic.
De Morgan's Laws[edit]
References[edit]
- Boolean Algebra (Wikipedia)
- De Morgan's Laws (Wikipedia)
- Logic Gates (Wikipedia)