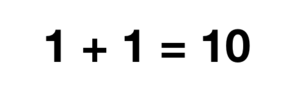Difference between revisions of "Alternative Base Addition"
From Coder Merlin
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
* [[W1011 Number Systems]] | * [[W1011 Number Systems]] | ||
== Addition (Decimal System) == | == Addition (Decimal System) == | ||
Addition is a basic (and critical) operation. Addition is '''commutative''', meaning that the order of the operands does ''not matter'' | Addition is a basic (and critical) operation. Important properties of addition include: | ||
* Addition is '''commutative''', meaning that the order of the operands does ''not matter'' | |||
** <math>a + b = b + a</math> | |||
* Addition is '''associative''', meaning that when we're adding more than two operands, the order that we perform the addition does ''not matter'' | |||
** <math>(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)</math> | |||
* The '''identity element''' for addition, also termed the '''additive identity''', is zero | |||
** <math>a + 0 = a</math> | |||
* The operator for addition is the plus (<math>+</math>) sign | |||
* The operands for addition are called '''addends''' | |||
There are a few simple rules when adding non- | Let's review how we perform addition in the number system with which we are most familiar, the decimal system. | ||
* | |||
There are a few simple rules when adding non-negative, whole numbers: | |||
# Align the addends vertically, flush right. (This step ensures that the ''position multiplier'' is the same for both addends in each column.) | |||
# Starting from the right-most column, add the two digits. If the sum exceeds the quantity that can be represented with a single digit, ''carry'' a one to the column to the left. | |||
# Repeat the process with the column to the left until reaching the final column. | |||
Let's look at a few examples: | |||
{| | |||
|style="width: 70%;" | To add <math>3 + 5</math> we: | |||
* align the digits vertically | |||
* add the right-most (and only column), yielding 8. Because this is less than the quantity that can be represented by a single digit, we have no carry. | |||
* done | |||
|style="width: 30%;" | | |||
{| class = "wikitable" | |||
| ''carry'' | |||
| 0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| ''addend'' | |||
| | |||
| 3 | |||
|- | |||
| ''addend'' | |||
| | |||
| 5 | |||
|- | |||
| ''sum'' | |||
| | |||
| 8 | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
== Topic Headers == | == Topic Headers == | ||
Revision as of 09:35, 19 July 2019
Within these castle walls be forged Mavens of Computer Science ...
— Merlin, The Coder
Prerequisites[edit]
Addition (Decimal System)[edit]
Addition is a basic (and critical) operation. Important properties of addition include:
- Addition is commutative, meaning that the order of the operands does not matter
- Addition is associative, meaning that when we're adding more than two operands, the order that we perform the addition does not matter
- The identity element for addition, also termed the additive identity, is zero
- The operator for addition is the plus () sign
- The operands for addition are called addends
Let's review how we perform addition in the number system with which we are most familiar, the decimal system.
There are a few simple rules when adding non-negative, whole numbers:
- Align the addends vertically, flush right. (This step ensures that the position multiplier is the same for both addends in each column.)
- Starting from the right-most column, add the two digits. If the sum exceeds the quantity that can be represented with a single digit, carry a one to the column to the left.
- Repeat the process with the column to the left until reaching the final column.
Let's look at a few examples:
To add we:
|
|
Topic Headers[edit]
Key Concepts[edit]
Exercises[edit]
References[edit]
- Addition (Wikipedia)